Remote patient monitoring (RPM) has become a crucial aspect of modern healthcare, enabling medical professionals to observe and manage patient health beyond the walls of hospitals and clinics. Wearable technology is at the heart of this shift, providing continuous real-time data on vital signs, supporting early diagnosis, and enhancing the management of chronic conditions—ultimately improving patient outcomes and reducing hospital readmissions.
How wearable devices are transforming sports and fitness training is another powerful example of their growing influence. In athletics and personal fitness, these devices offer insights into performance metrics such as heart rate zones, recovery rates, and physical exertion levels. By leveraging this data, athletes and fitness enthusiasts can customize their workouts, monitor fatigue, and optimize training plans—promoting efficiency, preventing injury, and maximizing overall results.
How Wearable Tech Supports Remote Patient Monitoring
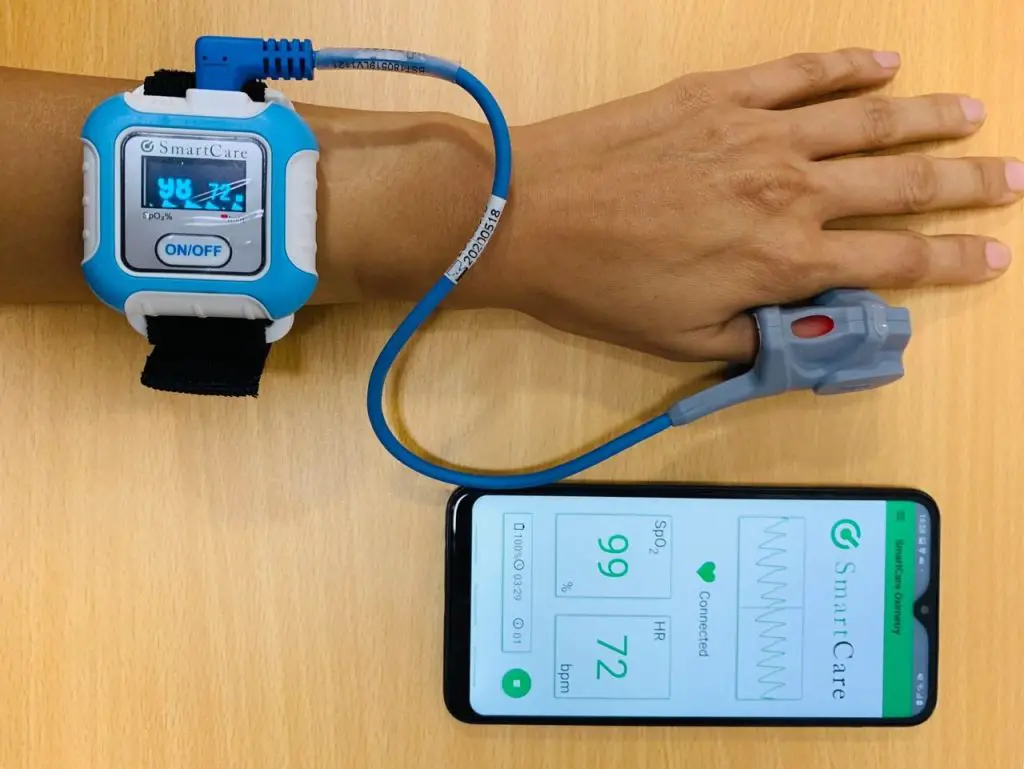
Wearable devices are equipped with sensors that monitor various health metrics such as heart rate, blood pressure, glucose levels, and oxygen saturation. These tools continuously gather physiological data and transmit it to healthcare providers, enabling early intervention before complications escalate. For instance, wearable ECG monitors can detect abnormal heart rhythms and notify physicians of potential atrial fibrillation before symptoms become critical. Likewise, smartwatches with SpO₂ sensors assist in tracking oxygen saturation in patients with respiratory issues like chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), supporting more proactive care.

The science behind wearable health trackers: how accurate are they? This question remains central to the trust and effectiveness of these tools. While wearables offer tremendous potential, their accuracy can vary depending on factors such as sensor quality, placement, and user movement. Researchers and developers are continuously working to refine the precision of these devices, ensuring that the health data they provide is reliable enough for clinical decision-making and not just general wellness tracking.
Benefits of Remote Patient Monitoring Wearables
1. Early Detection and Prevention
One of the biggest advantages of wearable tech in RPM is early disease detection. Conditions such as hypertension, diabetes, and heart disease can be monitored remotely, allowing healthcare professionals to intervene before emergencies occur.
2. Chronic Disease Management
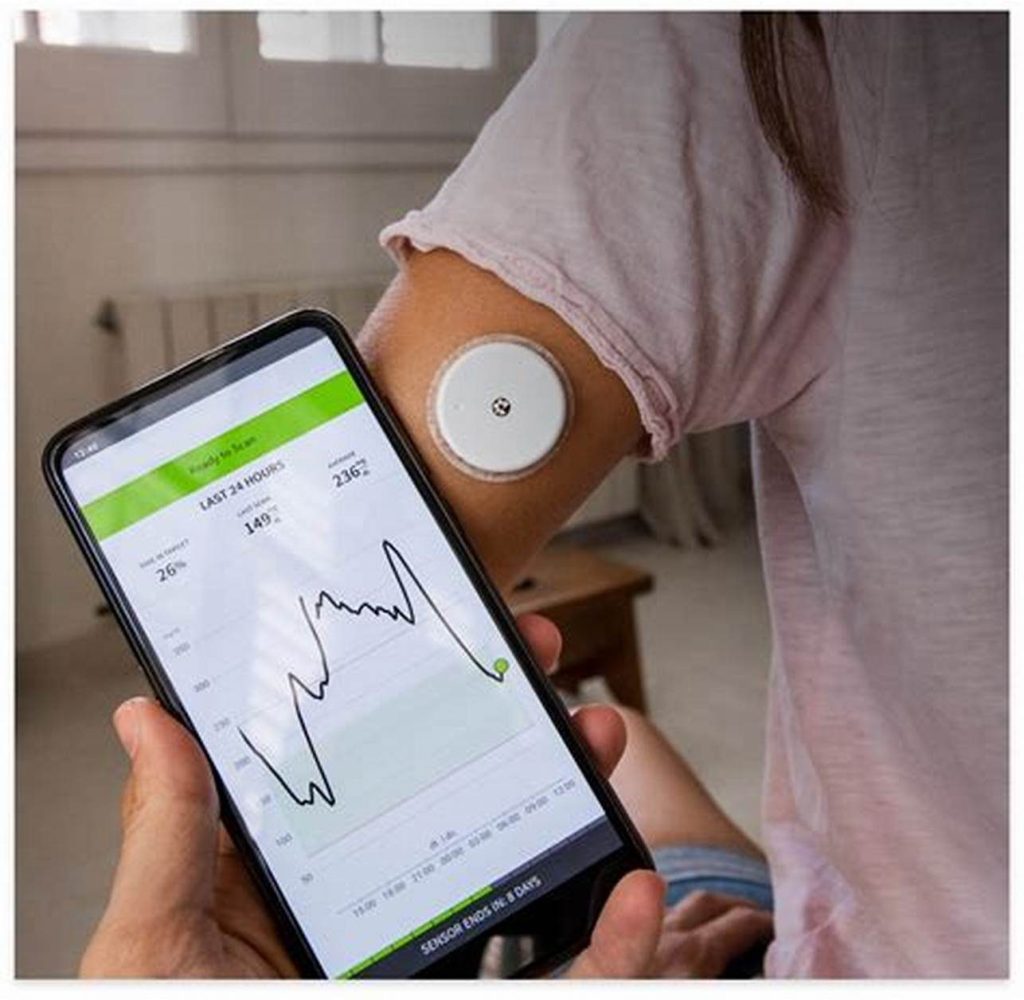
Patients with chronic conditions benefit significantly from continuous monitoring. Wearables help doctors track long-term trends in blood sugar levels for diabetics, monitor heart rate variability for cardiovascular patients, and ensure medication adherence through smart reminders.
3. Reduced Hospital Visits and Healthcare Costs
By providing remote monitoring, wearables reduce the need for frequent hospital visits, making healthcare more accessible and cost-effective. This is especially beneficial for elderly patients, those in rural areas, and individuals with mobility challenges.
Challenges and Considerations
While RPM wearables offer many benefits, challenges remain. Data privacy and cybersecurity are major concerns, as personal health data must be transmitted and stored in compliance with strict regulations. Additionally, many consumer-grade wearables lack the clinical accuracy of medical-grade devices, highlighting the need for improved validation, oversight, and standardization to ensure safe integration into healthcare systems.
How home automation is changing real estate and property value is also becoming a key consideration in modern housing. Homes equipped with smart health technologies—such as wearable-linked monitoring systems, automated lighting, climate control, and security—are increasingly seen as more desirable. These features enhance safety, convenience, and energy efficiency, often leading to higher property values and making homes more attractive to tech-savvy and aging populations alike.
Conclusion
Wearable technology is revolutionizing healthcare by making remote patient monitoring more effective and accessible. As technology continues to evolve, we can expect even greater accuracy, AI-driven insights, and better integration with telemedicine platforms. This advancement will not only improve patient outcomes but also reduce the burden on healthcare systems, making quality care available to more people than ever before.