Introduction
Imagine a world where your old smartphone, laptop, or wearable device doesn’t end up as e-waste but simply decomposes like a fallen leaf. Sounds like something out of a sci-fi novel, right? Well, it’s closer to reality than you might think. Biodegradable electronics, also known as transient electronics, are emerging as a game-changer in the tech industry. These innovative devices are designed to perform their function and then naturally break down, reducing environmental impact. But how exactly do they work, and what does the future hold for this groundbreaking technology?
What Are Biodegradable Electronics?
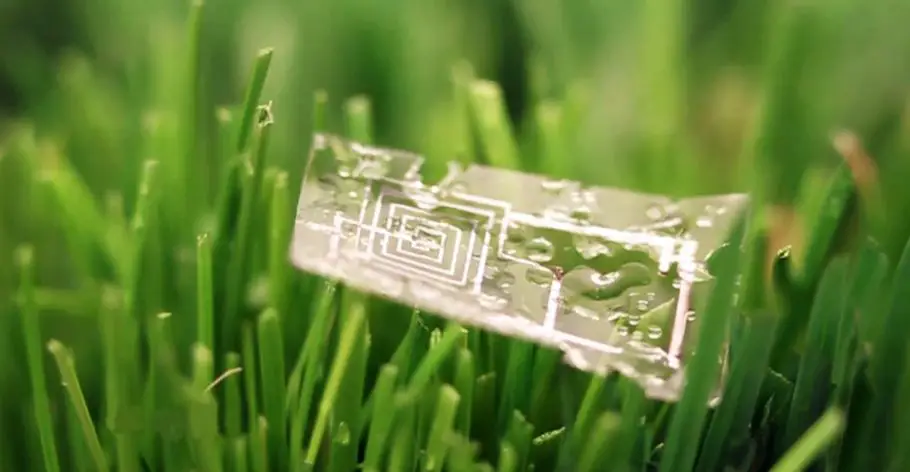

This refer to electronic devices designed to decompose naturally after their functional lifespan. Unlike traditional electronics, which contribute to massive amounts of e-waste, these devices use materials that break down safely in the environment. The concept revolves around sustainability and reducing electronic pollution.
Why Do We Need Biodegradable Electronics?
1. Tackling E-Waste
The world generates over 50 million tons of electronic waste annually, and only a fraction of it is properly recycled. The majority ends up in landfills, leaching toxic chemicals into the soil and water. Biodegradable electronics can significantly reduce this burden.
2. Reducing Toxicity
Traditional electronic components contain hazardous materials like lead, mercury, and cadmium. When disposed of improperly, these substances pose severe health risks. Biodegradable electronics eliminate the need for such harmful materials.
3. Promoting Sustainability
With increasing concerns about climate change and sustainability, industries are looking for greener alternatives. Biodegradable electronics align perfectly with the global push for sustainable development.
How Do Biodegradable Electronics Work?
1. Biodegradable Materials
These electronics are made from organic and naturally occurring materials, such as:
- Silk proteins – Used in flexible circuits.
- Magnesium – A biodegradable metal that dissolves safely in water.
- Cellulose – A plant-based material used for electronic substrates.
- Zinc oxide – Used in sensors and semiconductors.
2. Dissolvable Circuits
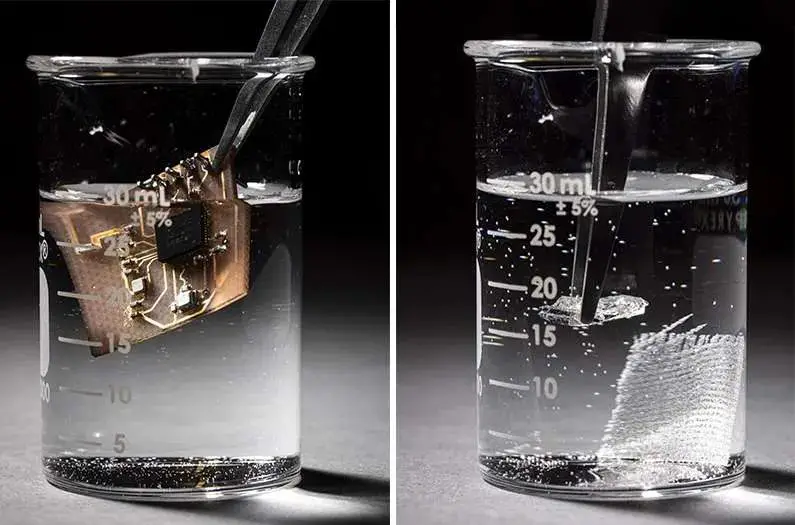
Unlike traditional circuits made from silicon and plastic, biodegradable electronics use dissolvable materials. These circuits can function like regular electronics but break down in response to environmental triggers like water or heat.
3. Biodegradable Batteries
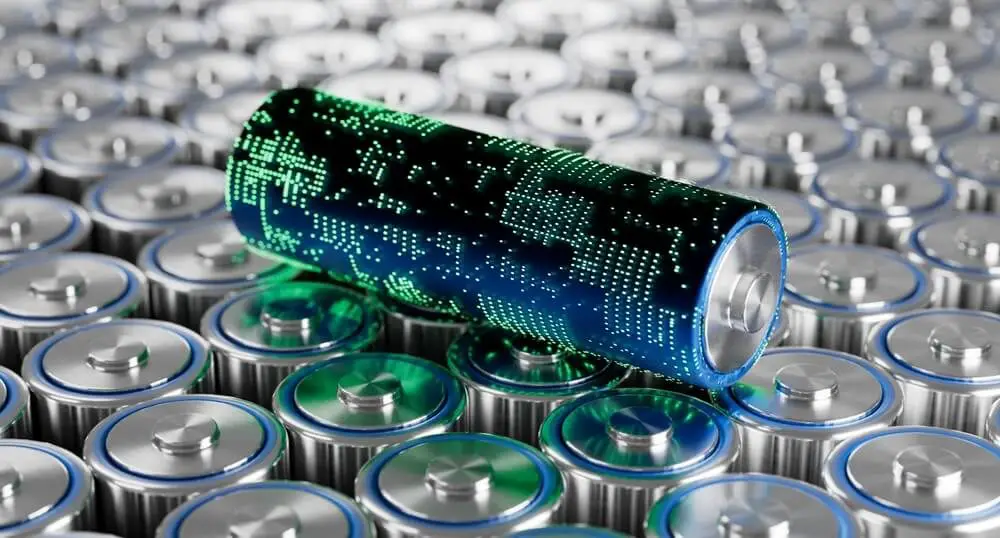

One of the biggest challenges in biodegradable electronics is energy storage. Researchers are developing biodegradable batteries made from non-toxic electrolytes and organic materials that decompose naturally after use.
Applications of Biodegradable
1. Medical Implants and Devices
Biodegradable electronics are revolutionizing the medical industry. Imagine a temporary pacemaker that dissolves inside the body once its job is done no need for surgical removal! This technology is already being explored for drug delivery, monitoring devices, and bioresorbable sensors.
2. Wearable Tech
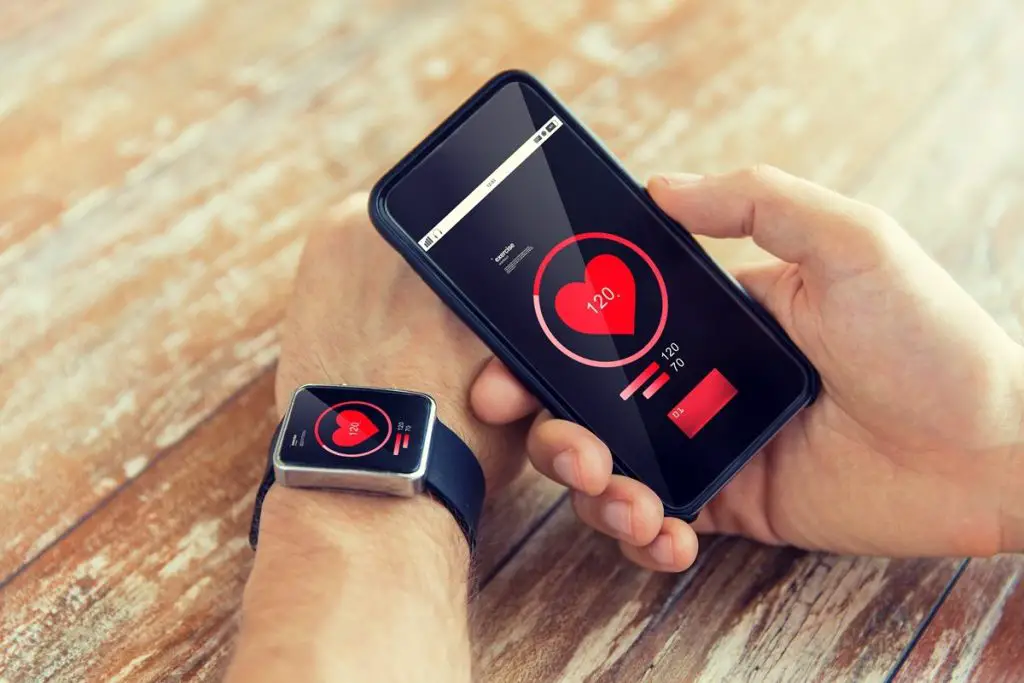

Smartwatches and fitness trackers made from biodegradable materials could significantly reduce e-waste. These devices could be designed to decompose naturally after their functional lifespan, making them more environmentally friendly.
3. Environmental Sensors

Researchers are developing biodegradable sensors that monitor environmental factors like air and water quality. These sensors can be deployed in remote areas and naturally degrade once they’ve served their purpose.
Using AI for Predicting Supply Chain Disruptions in Manufacturing
4. Consumer Electronics

Imagine a smartphone that lasts for a few years and then dissolves into harmless materials rather than ending up in a landfill. Companies are already exploring biodegradable components for phones, tablets, and laptops.
5. Military and Defense Applications

The military often uses electronic devices for temporary missions. Biodegradable electronics could ensure that sensitive tech doesn’t fall into the wrong hands while also reducing battlefield waste.
How Cloud Computing is Revolutionizing Education Accessibility
Challenges and Limitations
1. Durability Issues
Biodegradable materials must be strong enough to function efficiently while also being capable of breaking down when needed. Balancing these properties remains a challenge.
2. Mass Production Constraints
The technology is still in its early stages, and scaling up production while keeping costs low is a major hurdle.
3. Limited Lifespan
Since biodegradable electronics are designed to degrade, ensuring they last long enough for practical applications is a concern.
4. Energy Efficiency
Creating biodegradable batteries that provide sufficient power while decomposing safely is a complex challenge.
The Future of Biodegradable
Despite the challenges, researchers and tech companies are making significant strides. Scientists are exploring new materials and improving production techniques to make biodegradable electronics a mainstream reality.
1. Advancements in Material Science
Innovative materials like protein-based semiconductors and organic polymers are paving the way for more efficient biodegradable electronics.
2. Collaboration with Tech Giants
Companies like Google, Apple, and Samsung are showing interest in sustainable tech solutions. Their involvement could accelerate the adoption of biodegradable electronics in mainstream consumer products.
3. Government Regulations and Incentives
With stricter environmental regulations, governments worldwide are encouraging sustainable practices. Incentives for biodegradable electronics could drive investment and research in this field.
4. Integration with IoT and AI
Imagine biodegradable IoT sensors that collect and transmit data before breaking down, eliminating the need for retrieval or disposal. AI could further optimize the efficiency and application of these devices.
Conclusion
have the potential to revolutionize the tech industry and significantly reduce environmental harm. While challenges remain, rapid advancements in material science and growing sustainability efforts make it likely that we’ll see widespread adoption in the coming years. From medical implants to wearable tech and consumer electronics, this innovation could reshape the way we use and dispose of technology. The future of tech isn’t just about being smarter it’s about being greener too!
FAQs
1. Are biodegradable electronics commercially available?
Currently, biodegradable electronics are still in the research and development phase. Some prototypes exist, but widespread commercial availability is still a few years away.
2. How long do biodegradable take to decompose?
The decomposition time varies depending on the materials used. Some devices break down in a few days, while others may take months.
3. Can electronics replace traditional electronics completely?
Not entirely, at least not yet. Traditional electronics still have advantages in durability and performance. However, biodegradable electronics could become a viable alternative for certain applications.
4. Are biodegradable electronics expensive?
At present, they are more expensive due to limited production and specialized materials. However, costs are expected to decrease as the technology advances.
5. What industries will benefit most from biodegradable electronics?
The medical, environmental, and military sectors are among the biggest beneficiaries, but consumer electronics and IoT applications will also see significant advantages.
